- Home
- Request for Quote
- Products
- Variable Frequency Drive Systems and Controls
- AC Variable Frequency Drives
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Overview
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Technical Specifications
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Ratings, Types, Voltages and Construction – Prices
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Dimensions, Weight and Noise
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Interface and Options (prices)
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Technical Data
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Control Connections
- ABB ACS350 General Machinery Drives :: Overview
- ABB ACS350 General Machinery Drives :: Technical Specifications
- ABB ACS350 General Machinery Drives :: Ratings, Types, Voltages and Construction
- ABB ACS350 General Machinery Drives :: Dimensions, Weight and Noise
- ABB ACS350 General Machinery Drives :: Interface and Options (prices)
- ABB ACS350 General Machinery Drives :: Technical Data
- ABB ACS350 General Machinery Drives :: Control Connections
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Overview
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Hardware Description
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Standard Features and Options
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Specifications
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: 230V Ratings (pricing)
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: 380V Ratings (pricing)
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: 480V Ratings (pricing)
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Dimensions: ACS550 NEMA 1 R1 through R6 Frame Size
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Dimensions: ACS550 NEMA 12 R1 through R6 Frame Size
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Dimensions: ACS550-02 NEMA 1 R7 Frame Size
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Dimensions: ACS550-02 NEMA 1 R8 Frame Size
- ABB ACS550 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Dimensions: ACS550-U2 NEMA 1 R7 & R8 Frame Size
- ABB ACS 600 Adjustable Speed AC Drives
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Overview
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Standard Features / Available Options and Software
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Specifications
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: Basic Type Code Information
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: 230V Ratings (pricing)
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: 380V Ratings (pricing)
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: 460V Ratings (pricing)
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: ACS 800-U2 NEMA 1 R7 & R8 Frame Size and ACS 800-02+C111 IP21 (NEMA 1) R7 & R8 Frame Size
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: ACS 800 NEMA 1/12 R2 through R6 Frame Size
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: ACS 800-02 NEMA 1 R7 & R8 Frame Size
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: ACS 800-U4 Module R7 Frame Size
- ABB ACS800 AC Variable Frequency Drive :: ACS 800-U4 Module R8 Frame Size
- ABB ACS880 Industrial Low Voltage AC Drives
- ABB ACS880 AC Drives – Technical Data
- Wall-mounted single drives, ACS880-01
- ABB ACS880 Ratings, types and voltages
- ABB ACS880 AC Drives – Dimensions & Connectivity
- ABB ACS880 AC Drives – Standard Software
- ABB ACS880 AC Drives – Intuitive Human-Machine Interface
- ABB ACS880 AC Drives – Integrated Safety
- ABB ACS880 AC Drives – Flexible Connectivity
- Input/output Modules, Speed Feedback Interfaces & Communication Modules
- ABB Softstarters, Type SSM, Medium Voltage, 2300-13,800V :: Description
- ABB Type SSM Softstarters – Medium Voltage, 2300-13,800V :: General Information
- ABB Type SSM Soft Starters – Medium Voltage, 2300 – 13,800V :: Catalog Numbers
- ABB Soft Starters, Type SSM – Medium Voltage, 2300-13,800V :: Technical Data
- ABB Softstarters, Type SSM, Medium Voltage, 2300-13,800V :: Approx. Dimensions
- Yaskawa AC Drives
- AuCom Soft Starters
- Emerson Industrial Automation (Control Techniques and Saftronics) AC Drives
- Control Techniques – Commander SE AC Drive
- Control Techniques – Commander SK AC Drive
- Commander SK :: Features
- Commander SK :: Terminal Diagram and Description
- Commander SK :: Specifications and Dimensions
- Commander SK – Options :: Overview
- Commander SK – Options :: Configuration and Programming
- Commander SK :: Operator Interface
- Commander SK :: Power Accessories
- Commander SK :: Environmental Protection and Cable Management
- Commander SK :: Input / Output
- Commander SK :: Communication
- Commander SK :: Programming Software
- Control Techniques – Commander SX AC Drive
- Commander SX :: Features, Ratings, Prices and Ordering
- Commander SX :: Terminal Diagram and Description
- Commander SX:: Specifications and Dimensions
- Commander SX :: Options – Overview / Drive Configuration and Programming
- Commander SX :: Communication / Operator Interface
- Commander SX :: Power Accessories
- Commander SX :: Input/Output and Communication
- Control Techniques – Unidrive SP AC Drive
- Unidrive SP :: Features
- Unidrive SP :: Ratings, Prices & Ordering – Wall Mount
- Unidrive SP :: Ratings, Prices & Ordering – Free Standing Cubicle
- Unidrive SP :: Unidrive SP Regen Mode
- Unidrive SP :: Terminal Diagram and Description
- Unidrive SP :: Specifications and Dimensions
- Unidrive SP :: Options – Overview
- Unidrive SP :: Operator Interface
- Unidrive SP :: Power Accessories
- Unidrive SP :: Option & Feedback Modules
- Unidrive SP :: Option Input / Output Modules
- Unidrive SP :: Option Application / Programming Modules
- Unidrive SP :: Option Communication Modules
- Unidrive SP :: Drive Configuration and Programming
- Unidrive SP :: Application Programming Software
- Unidrive SP :: Pre-packaged Solutions
- Saftronics GP10 AC Drives
- Saftronics GP10 – Pricing, Dimensions & Weights
- Saftronics GP10 – Optional DC Link Reactors
- Saftronics GP10 – Options & Accessories
- Saftronics GP10 – Palm Pilot Saflink Kit
- Saftronics GP10 – SR10 Radio Modem Kit
- Saftronics GP10 – Relay Output Card
- Saftronics GP10 – Digital I/O Interface Card
- Saftronics GP10 – Analog I/O Interface Card
- Saftronics GP10 – SF-10 Ethernet Module
- Saftronics GP10 – Interface Option Card
- Saftronics GP10 – Under Torque Detection Option
- Saftronics GP10 – 24 VDC or 24/120 VAC Interface
- Saftronics GP10 – Air Pressure Sensor + V/I Converter Output Card
- Saftronics GP10 – HMI Pump Controller
- Saftronics GP10 – SDBU – Dynamic Brake Module
- Saftronics GP10 – 208-230V Dynamic Brake Packages
- Saftronics GP10 – 460V Dynamic Brake Packages
- Saftronics GP10 – Ratings Efficiency & Watts Loss
- Saftronics GP10 – Standard Specifications
- Saftronics GP10 – Basic Connection Diagram
- Saftronics GP10 – Basic Connection Diagram to PLC
- Saftronics GP10 – Basic Connection Diagram (Europe)
- Saftronics GP10 – Basic Connection to PLC (Europe)
- Saftronics S10 AC Drives
- Saftronics S10 – Options and Accessories
- Saftronics S10 – Standard Specifications
- Saftronics S10 – Dimensions
- Saftronics S10 – Dimensions – Part Number: S102002 – S102003 & S104001 – S104003
- Saftronics S10 – Dimensions – Part Number: S102F25 – S102001
- Saftronics S10 – Dimensions — Part Number: S102F25 – S102001 no Operators
- Saftronics S10 – Dimensions – Part Number: S102002-2003 & S104001-4003
- Saftronics S10 – Basic Wiring Diagram
- Saftronics CV10 AC Drives
- Saftronics CV10 – Part Numbers, Dimensions & Weights
- Saftronics CV10 – LED Keypad with Speed Pot
- Saftronics CV10 – LCD Keypad (supports 5 Languages)
- Saftronics CV10 – Keypad Extension Cable
- Saftronics CV10 – Communication Option Cards
- Saftronics CV10 – Bi-Polar Speed Reference Option Card
- Saftronics CV10 – Standard Specifications
- Saftronics CV10 – Ratings Efficiency and Watts Loss
- Saftronics CV10 – Dimensions Frame 1 – IP20 (Open Chassis)
- Saftronics CV10 – Dimensions Frame 1 – NEMA 1
- Saftronics CV10 – Dimensions Frame 2 – IP20 (Open Chassis)
- Saftronics CV10 – Dimensions Frame 2 – NEMA 1
- Saftronics CV10 – Dimensions Frame 3 – IP20 (Open Chassis)
- Saftronics CV10 – Dimensions Frame 3 – NEMA 1
- Saftronics CV10 – Basic Wiring Diagram
- Saftronics VG10 AC Drive
- Saftronics VG10 – Pricing, Dimensions & Weights
- Saftronics VG10 – Optional DC Link Reactors
- Saftronics VG10 – Options and Accessories
- Saftronics VG10 – Palm Pilot Saflink Kit
- Saftronics VG10 – Relay Output Card
- Saftronics VG10 – SR10 Radio Modem Kit
- Saftronics VG10 – Digital I/O Interface Card
- Saftronics VG10 – Analog I/O Interface Card
- Saftronics VG10 – SF-10 Ethernet Module
- Saftronics VG10 – PGX Encoder Feedback Card
- Saftronics VG10 – Encoder + Analog Output Card
- Saftronics VG10 – PG Feedback Card SOPCG11SPG
- Saftronics VG10 – PG Feedback Card SOPCG11SPG2
- Saftronics VG10 – Synchronized Operation Card
- Saftronics VG10 – 24 VDC or 24/120 VAC Interface Card Kit
- Saftronics VG10 – Air Pressure Sensor + V/I Converter Output Card
- Saftronics VG10 – SDBU – Dynamic Brake Module
- Saftronics VG10 – 208-230V Dynamic Brake Packages
- Saftronics VG10 – 460V Dynamic Brake Packages
- Saftronics VG10 – Ratings Efficiency and Watts Loss
- Saftronics VG10 – Standard Specifications
- Saftronics VG10 – DC Link Reactor 100 HP and Above
- Saftronics VG10 – Basic Connection Diagram (Sink Logic, Mainly America)
- Saftronics VG10 – Basic Connection Diagram to PLC (Sink Logic, Mainly America)
- Saftronics VG10 – Basic Connection Diagram (Source Logic, Mainly Europe)
- Saftronics VG10 – Basic Connection Diagram to PLC (Source Logic, Mainly Europe)
- Saftronics PC10 (Obsolete) AC Drives
- Saftronics PC10 – Options & Accessories
- Saftronics PC10 – SF-10 Ethernet Module Kit
- Saftronics PC10 – 24 VDC or 24/120 VAC Input + Relay Option Card
- Saftronics PC10 – 24 VDC or 24/120 VAC Interface Card Kit (PC10, GP10, or VG10 Inverter)
- Saftronics PC10 – Relay Output Card
- Saftronics PC10 – HMI Pump Controller
- Saftronics PC10 – PC10 120 VAC Option Card
- Saftronics PC10 – Palm Pilot Saflink Kit
- Saftronics PC10 – Dynamic Braking
- Saftronics PC10 – Drive Ratings Efficiency and Watts Loss
- Saftronics PC10 – Standard Specifications
- Saftronics PC10 – Part Number: PC102F12-9, PC102F25-9, PC102F50-9 & PC102001-9
- Saftronics PC10 – Part Number: PC102002-9, PC102003-9, PC104F50-9, PC104001-9, PC104002-9 & PC104003-9
- Saftronics PC10 – Part Number: PC102005-9 & PC104005-9
- Saftronics PC10 – Part Number: PC102007-9, PC102010-9, PC104007-9 & PC104010-9
- Saftronics PC10 – NEMA 1 Kit Dimensions
- Saftronics PC10 – Basic Wiring Diagram
- Fincor 5700 Series (Obsolete) AC Drive
- Fincor 5740 Series (Obsolete) AC Drive
- Fincor 5750 Series (Obsolete) AC Drives
- Motortronics Soft Starters
- SOLCON Soft Starters
- SOLCON RVS-DN Digital Soft Starter with Advanced Motor Protection
- Solcon HRVS-DN Digital Soft Starter with Advanced Motor Protection
- Solcon HRVS-TX Digital Transformer Soft Starter
- SOLCON RVS-AX Analog Soft Starters
- SOLCON Solstart Plus Analog Soft Starters
- SOLCON RVS-BX Basic Soft Starter with Built-In Bypass
- SOLCON RVS-DX Digital Soft Starter with Built-In Bypass
- SOLCON RVS-EX Digital Soft Starter for Explosion Proof motors with Built-In Bypass
- SOLCON SEM-N Rugged Soft Starter for Naval and Military Specifications
- SOLCON SOLSTART Miniature Analogue Soft Starter
- SOLCON SOLSTART 1P Single Phase Analogue Soft Starter
- SOLCON SOLBRAKE DC Injection Brake Soft Starter
- Magnetek – Soft Starters
- WEG Variable Frequency Drives, Controls and Motors
- ABB ACS150 Component Drives :: Overview
- DC Variable Speed Drives
- DC Drive Fundamentals
- ABB DCS 400 Digital DC Converter Drive
- ABB DCS 500 DC Drive
- ABB DCS800 DC Drives Overview
- DCS800 – Power Converter Modules
- DCS800 Panel Drive
- DCS800 Enclosed Converters
- DCS800 Rebuild and Upgrade Kits
- Adaptive Programming and Start-up Assistants
- DriveWindow Light – Startup and Maintenance Tool
- DCS800 Commissioning Macros
- DCS800 Firmware
- DCS800 Technical Specifications
- Current Ratings – Modules – Non-Regenerative
- Current Ratings – Modules – Regenerative
- Current Ratings – Modules – DCS800-EP Panel Drive
- DCS800 Dimensions and Weights
- DCS800 Technical Diagram
- DCS800 Plug-in Options
- DCS800 Feedback Options
- DCS800 Communication Options – Fieldbus Control
- DCS800 External Field Supply
- ABB DCS800-EP replaces Reliance FlexPak® 3000 – 230V Drive Cross Reference
- ABB DCS800-EP – 460V Drive Cross Reference
- ABB DCS800-EP – Options Cross Reference
- ABB DCS800-EP – Product Differences and Remedies – Hardware
- ABB DCS800-EP – Product Differences and Remedies – Control/Interface & Features
- ABB DCS800-EP – Drive Dimensions
- ABB DCS800-EP – Installation Procedure – Wiring and Configuration
- ABB DCS800-EP – Parameter Cross-Reference
- FINCOR Series 2600/2610 DC Drives
- 50 Amp & 90 Amp DC Field Regulators
- Mentor II | Quantum III | FXM5 Change of Status
- SIMOREG 6RA24 Siemens DC Drive Features
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Siemens Variable Speed DC Drive Description and Base Drive Catalog Numbers
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Siemens DC Drive Features
- SIMOREG 6RA70 DC Master Design & Operation – Converters
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Parameterization Devices
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Software Structure
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Closed-Loop Functions in Armature Circuit
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Closed-Loop in Field Circuit
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Optimization Run
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Monitoring & Disgnosis
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Functions of Inputs & Outputs
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Safety Shutdown (E-STOP)
- SIMOREG 6RA70 Design & Operation – Serial Interface
- 1000 Hp DC Variable Speed Drive System
- 3000 Hp DC Variable Speed Drive
- Permanent Magnet DC Motors
- SCR Drive Controllers (SCR-Silicon Controlled Rectifier)
- Custom Electric Control Panel Shop
- GE AC & DC Motors (G.E. Motors – General Electric AC & DC Motor)
- GE X$D Ultra® NEMA Premium Efficiency – TEFC AC Motors
- GE Kinamatic® Explosion Proof AC Motors
- GE Energy Saver® – TEFC Severe Duty AC Motors
- GE Kinamatic® General Purpose AC Motors
- GE Motors Energy Saver NEMA Premium Efficiency – ODP AC Motors
- GE ValueLine™ EPAct Efficiency – TEFC AC Motors
- GE ValueLine™ EPAct Efficiency – ODP AC Motors
- GE Permanent Magnet Custom DC Motors
- GE ValueLine™ Vertical Hollow Shaft AC Motors
- GE Permanent Magnet Standard DC Motors
- GE ASD Inverter Duty AC Motors
- G.E. Permanent Magnet Washdown DC Motors
- Avtron – Drives, Measurement and Tachs
- Avtron – Adjustable Speed Drives and Drive Systems
- Avtron – Speed and Length Measurement
- Avtron – Tachs, Tachometers, Encoders, Rotary Pulse Generators
- Avtron – Sales Literature and Instruction Sheets
- Avtron – Classic Tach Models
- Avtron – Price Quotation Request Form
- Avtron – Tachometers Availability
- Avtron – Heavy, Mill-Duty Encoders
- Avtron – Setting Air Gap on M285 Sensors
- Avtron – M4 Universal Encoder
- Avtron – M56, M67, M85 THIN-LINE
- Avtron – M285QUAD Outline Drawing
- Avtron – Severe Duty Encoders
- Avtron – Mill-Duty Encoders
- Avtron – M3 Universal Encoder
- Avtron – M3 Applications
- Avtron – M3 Installation
- Avtron – M3 Specifications
- Avtron – Tach Accessories
- Avtron – Tach Solutions
- Avtron – Rugged Environments
- Avtron – Selection by Motor Frame Size
- Avtron – Adapter Kits Outline Drawings
- Avtron – Motors with Brakes
- Avtron – NEMA C Face Mounting
- Avtron – Market Specific Applications
- Dynapar Encoders and Tachs
- ACURO AI25 Encoders
- Acuro Series AI25 Absolute Encoder with DeviceNet Interface
- Acuro Series AI25 Absolute Encoder with Profibus Interface
- Acuro Series AI25 Absolute Encoder with Interbus Interface
- Acuro Series AI25 Absolute Encoder with BiSS Interface
- Acuto Series AI25 Optical Encoders with SSI Interface
- Acuro Series AI25 Absolute Encoder with Parallel Interface
- Acuro Series AD25 Drive Absolute Encoder
- Series R25 – Mill Duty, HOUSED Resolver
- Series 21/22 Heavy Duty Incremetal Encoders
- Series H20 Encoder
- Series HA25 Dynapar Heavy Duty Encoders
- Series HR25 Incremental Encoders
- Series HC25 Incremental Encoders
- Series H58 Heavy Duty Encoders
- Series H42 Heavy Duty Encoders
- Series HA725 Indusrtial Duty Encoders
- Series HD20 Optical Encoder
- Series HD25 Optical Encoder – Harsh Duty
- Series H56 Rotopulser Heavy Duty Encoders
- RIM Tach 6200 Digital Tachometer
- Series X25 Incremental Encoders
- Series 60 Rotopulser Incremental Encoders
- Series H20 Hub Shaft Encoders
- Series HSD25 Harsh Duty Optical Encoders
- Series HSD44
- Series HS20 Sealed Hollow Shaft Encoders
- Series HS35 Sealed Hollow Shaft Encoders
- The NEW HS35R
- Series HSD35 Shaftless Optical Encoder
- Series HSD37 Hollowshaft Rotary Encoder
- Series HSD38 Harsh Duty Optical Encoder
- Series DWD38 Heavy Duty Rotary Encoders
- SLIM Tach HS56 Incremental Encoder / Tachometer
- RIM Tach HS85 Digital Tachometer
- SLIM Tach SL56 Rotary Encoder
- SLIM Tach RL67 Incremental Rotary Encoder
- SLIM Tach SL85 Digital Tachometer
- SLIM Tach SL1250 Incremental Encoder
- RIM Tach 8500 Digital Tachometer
- RIM Tach 1250 Digital Tachometer
- Series R45 Rotopulser Incremental Encoders
- ACURO AI25 Encoders
- Spare Parts and Replacement Parts
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers)
- Services
- Projects
- Operator Stations by Joliet Technologies
- AC VFD, AC Controllers and DC VSD by Joliet Technologies
- Material Handling Modernization Project by Joliet Technologies
- 10 DC (SCR) Drive System :: Neptune Marine Oil & Gas
- Mermaid Offshore Services :: 4 DC (SCR) Drive Cabinets
- “Frontier Driller” Offshore Oil Rig :: DC (SCR) Drive Bays
- 1000Hp Siemens SIMOREG 6RA70 DC Variable Speed Drive Retro-Fit
- Smurfit-Stone: Corrugator Crew Sets Production Record
- Steel Slitting Line for Braner USA
- 1000HP DC Drive, Bow Thruster Application for Pegler Automation
- 1000HP DC Traction Motor Drive, Slurry Pump Application for Baker Hughes
- Siemens 6RA70 DC Drive and GE 752 Traction Motor to Hallett Materials
- ABB ACS 800 VFD to Applied Synergistic
- Two 200Hp Variable Speed DC Drives and Motors to JHT Electronics
- Substrate Technology Inc. :: Joliet Technologies, L.L.C.
- Wyco Tool Company
- Variable Frequency Drives and Controls for Food Processing and Bakery Machinery
- Information
- Guide to Harmonics with AC Variable Frequency Drives
- Variable Speed Drives – Application Information
- Reducing harmonics caused by variable speed drives
- FAQ – Variable Speed Drives Frequently Asked Questions
- EASA Electrical Engineering Handbook
- Part Winding Start
- 3Ph Motors, Single Speed
- 3Ph Motors, 2 Speed, Single Winding
- Connections for NEMA DC Motors
- Connections for NEMA DC Generators
- Field Polarities of DC Machines
- Maximum Locked-Rotor Currents – Three-Phase Squirrel Cage Motors
- NEMA Code Letters for AC Motors
- General Speed-Torque Characteristics
- Effect of Voltage unbalance on Motor Performance
- Starting Characteristics of Squirrel Cage Induction Motors
- Allowable Starts and Starting Intervals
- NEMA Size Starters for Three-Phase Motors
- Starter Enclosures
- NEMA Size Starters for Single-Phase Motors
- Determining the Polarization Index of Machine Windings
- Formulas for Electrical Motors
- Motor Application Formulas
- Glossary of Terms
- Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) Case Studies
- VFD Case Studies – ABB drives & motors help to launch lifeboats quickly and safely.
- VFD Case Studies – Paperboard mill benefits from using DC drives
- VFD Case Studies – ABB Drive cuts water pumping bill for semiconductor plant.
- VFD Case Studies – Insulation manufacturing process saves energy with ABB :: Joliet Technologies
- VFD Case Studies – ABB drives cut costs at MINI production plant
- VFD Case Studies – Film maker slashes costs with ABB drives
- VFD Case Studies – ABB drive cuts costs for wooden toy company
- VFD Case Studies – Close pump control doubles efficiency for West of Scotland Water
- VFD Case Studies – ABB Energy Appraisal Saves Money :: Joliet Technologies
- VFD Case Studies – Staggering energy savings prove value of professional audit
- VFD Case Studies – Soft starters save costs for mechanical engineers
- NEMA Frame Chart and T-Frame Chart :: Joliet Technologies
- Model 1681 Instruction Manual – Firing Circuits DC SCR Drives
- IGBT – Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors :: Joliet Technologies
- Blog
Blog
Ultimate Tips for Choosing the Right DC Motor Controller for Your Project
Choosing the right DC motor controller is a critical step in ensuring the success of any project that involves motorized systems. The DC motor controller is the brain behind the operation of DC motors, managing speed, direction, and torque. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in motor control systems, “Selecting the right DC motor controller can make or break your project's efficiency and reliability.” Her insights underscore the importance of understanding various factors such as compatibility, control method, and application requirements when making this choice.
In the rapidly evolving field of automation and robotics, the decision regarding which DC motor controller to use can significantly impact performance. Engineers and designers must consider how each controller will affect the overall functionality of their devices. Whether you are developing a simple hobby project or a complex industrial automation system, the right DC motor controller can optimize performance, enhance efficiency, and even prolong the lifespan of the motor. This guide will provide essential tips and insights to navigate the myriad options available in the market, helping you make an informed decision that meets your specific project needs.

Understanding DC Motor Controllers: Types and Applications
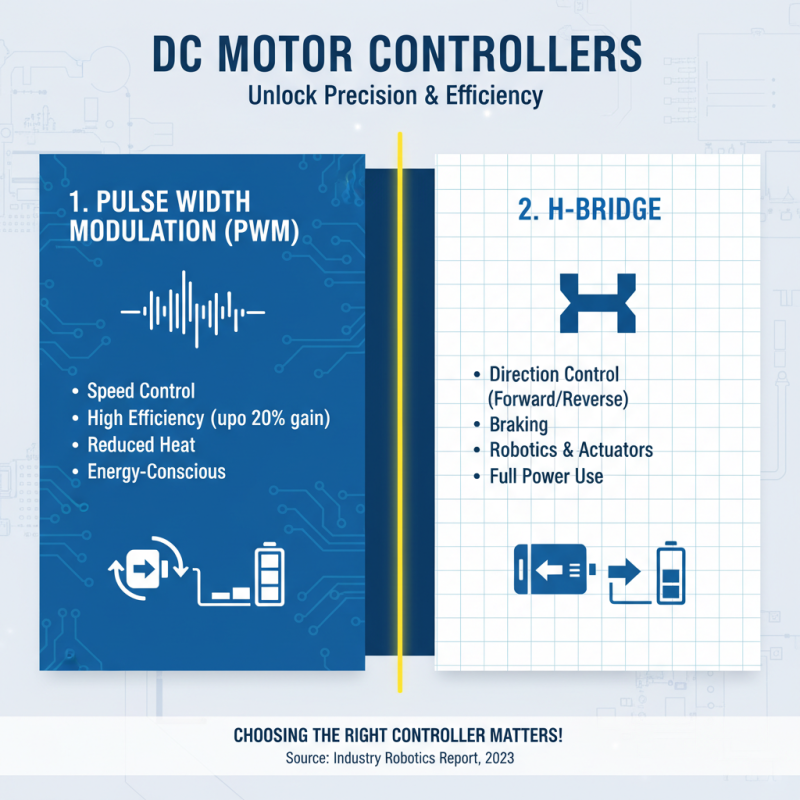
DC motor controllers play a crucial role in a variety of applications, from robotics to industrial automation. Understanding the types of DC motor controllers available can help project designers select the right one for their needs. Generally, there are two main types of controllers: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controllers and H-bridge controllers. PWM controllers adjust the power delivered to the motor by varying the pulse width of the voltage signals, which allows for efficient speed control and reduced heat generation. According to a recent industry report, PWM controllers can improve motor efficiency by up to 20%, making them a popular choice for energy-conscious designs.
H-bridge controllers, on the other hand, are renowned for their ability to control the direction of the motor's rotation, as they allow current to flow in both directions through the motor. This capability is fundamental in applications such as electric vehicles and robotics, where directional movement is essential. Data from the International Electrotechnical Commission indicates that demand for H-bridge controllers has been increasing, with a projected growth rate of over 15% annually in sectors utilizing robotics and automation. By understanding these types and their applications, engineers can make informed decisions, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in their projects.
Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a DC Motor Controller
When selecting a DC motor controller for your project, understanding key specifications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. One of the primary factors to consider is the current rating. A controller must be capable of handling maximum motor current under various load conditions. According to industry reports, a mismatch in current ratings can lead to inefficiencies or even damage the controller or the motor, potentially leading to costly repairs and downtime.
Another essential specification is the voltage output range of the DC motor controller. It should align with the voltage requirements of your motor to ensure proper operation. Data from recent market analysis indicates that motors operating around 12V, 24V, and 48V are prevalent across various applications, making it vital to choose a controller compatible with these voltage levels. Additionally, assessing the controller’s PWM (pulse-width modulation) frequency is important; higher frequencies can improve torque control and reduce audible noise, which is significant in applications demanding precision and quieter operation.
Lastly, consider the thermal management capabilities of the controller. Effective heat dissipation will prolong the life of both the motor and controller, particularly in high-load scenarios. Research shows that controllers with advanced thermal management features can sustain performance while minimizing the risks of overheating, which is a common failure point in DC motor setups. By focusing on these specifications, you can ensure that the selected motor controller meets both the functional requirements and operational longevity needed for your project.
Evaluating Control Methods: PWM vs. Voltage Control Techniques
When selecting the right DC motor controller for your project, understanding the different control methods available is crucial. Two of the most commonly used techniques are Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and voltage control. Each method has its own set of advantages and applications, making them suitable for different types of projects and performance requirements.
PWM control is particularly favored for its efficiency and precision. By rapidly switching the motor's power on and off, PWM can regulate the effective voltage and current supplied to the motor, allowing for fine speed adjustments without wasting energy in the form of heat. This method is ideal for applications requiring high-speed control and responsive action, such as in robotics or automated systems. The ability to achieve smooth acceleration and deceleration also makes PWM a preferred choice for many designers.
On the other hand, voltage control techniques offer a simpler implementation, particularly suited for applications where speed control is less critical. By directly varying the supply voltage, users can achieve speed adjustments, though this may lead to less energy efficiency compared to PWM. Voltage control can be more straightforward, requiring fewer components and enabling easier debugging in simpler applications. However, for projects demanding precise control over speed and torque, PWM will typically outperform voltage-based methods, leading to smoother operations and better overall performance.
DC Motor Control Techniques Comparison
Compatibility and Integration: Matching Your Controller to Motor Requirements

When selecting a DC motor controller, compatibility and integration are paramount factors that can significantly impact the success of your project. Understanding the voltage and current specifications of the motor is essential, as these parameters directly correlate with the controller’s capabilities. According to industry research, nearly 40% of project failures arise from mismatches between controllers and motors, highlighting the importance of careful selection. Engineers often recommend that the rated voltage of the motor should ideally match the output voltage specifications of the controller to prevent performance issues and potential damage.
Additionally, the communication interface of your motor controller plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless integration within your system. Many modern controllers support various protocols such as PWM, CAN, and RS-485, catering to different system architectures. A relevant study indicates that 65% of industrial automation projects experience delays due to integration difficulties, accentuating the need for controllers that offer flexible connectivity options. Properly assessing these factors not only enhances the operational efficiency of your motors but also streamlines troubleshooting and upgrades in the future, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes in your engineering endeavors.
Industry Benchmarks: Performance Metrics for DC Motor Controllers
When selecting a DC motor controller for your project, understanding key performance metrics is crucial. According to recent industry benchmarks, efficiency is one of the most critical factors, with leading controllers achieving efficiencies exceeding 90%. This level of efficiency not only ensures optimal power usage but also minimizes heat generation, which can prolong the lifespan of both the motor and the controller. In applications where precision and reliability are paramount, controllers should also demonstrate consistent performance across varying load conditions. Research indicates that high-quality controllers maintain stable operation with input voltage variations of up to 20%, providing confidence for project developers in dynamic environments.
Another vital metric is responsiveness, typically measured through the controller's ability to handle changes in speed and load. Manufacturers have reported that advanced DC motor controllers can achieve a response time of less than 10 milliseconds, making them ideal for robotics and automation applications where precise motor control is required. Additionally, performance under different environmental conditions contributes to a controller’s reliability; IP ratings are commonly used to benchmark this aspect. Controllers with a minimum IP54 rating are recommended for dusty or damp environments, ensuring durability and operational integrity.
By focusing on these metrics—efficiency, responsiveness, and environmental resilience—engineers can make informed decisions when selecting the right DC motor controller for their needs.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Importance of DC Motor Controllers in Modern Automation Systems
-

Unlocking the Power of VFD Motor Control for Energy Efficient Industrial Applications
-
2025 Top DC Motor Controller Solutions for Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
-

Top 10 AC Motor Speed Controllers to Enhance Your Efficiency in 2023
-
How to Optimize Energy Efficiency with Variable Frequency Drives: Key Insights and Data
-

Unlocking Efficiency: How Variable Speed Motors Transform Modern Machinery

